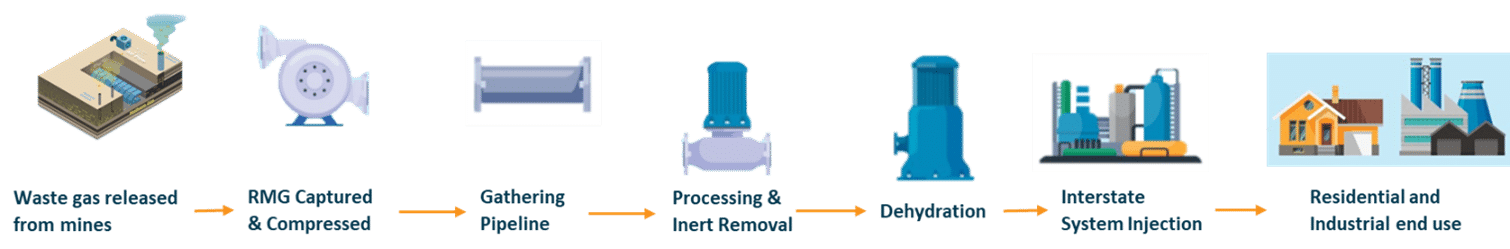
Remediated Mine Gas (RMG)
Remediated Mine Gas (RMG) is a product of captured and upgraded residual waste gases which are necessarily released from mines for safety purposes, keeping the underground conditions of mines below explosive limits. Capturing, upgrading, and utilizing this waste gas from mining activities is essential to Climate Targets, as RMG prevents the release of unabated methane emissions into the atmosphere and provides energy consumers (power producers, data centers, chemical manufactures, etc.) a flexible low carbon intensity option that can displace the use of convention fossil resources.
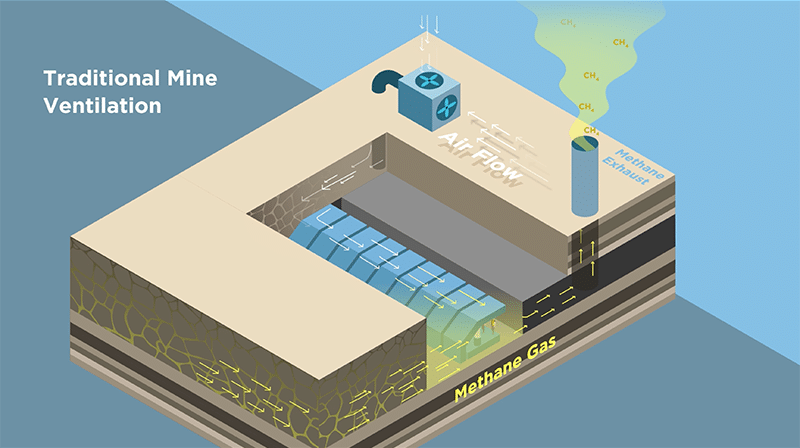
Mines are responsible for nearly 10% of U.S. methane emissions. There are no regulatory requirements in the U.S. for the abatement of mine methane emissions, which are a potent greenhouse gas, meaning that common business practice is to vent mine gas to ensure mine safety. Methane emissions from underground mines continue for decades after mines are closed and abandoned and can produce significant emissions as these gases will continue to build even after mine operations cease. The overwhelming majority of mines vent methane to the atmosphere, with only 3 of the 560 active U.S. mines reporting pipeline injection use of RMG in 2023 as the cost to capture is typically a barrier. According to the Global Energy Monitor, the methane released from active U.S. mines was estimated to have been 82.9 million MT CO2e in 2022. In 2023, less than 0.1% of the 30,771 abandoned mines registered methane capture projects. While abandoned mines are not required to report their emissions, the EPA’s Inventory Analysis estimates that abandoned mines emitted 6.3 million MT CO2e of uncaptured methane in 2022. Methane emissions from abandoned mines are estimated to increase 8-fold by the end of the century.1
CNX’s solution for RMG follows the same principles of residual waste methane capture, processing, compression, and transportation of methane to market long established in Renewable Natural Gas production from landfill, food waste, and manure projects. By capturing this waste, processing it up to pipeline specifications, and delivering it to the market as RMG, CNX is converting a potent greenhouse gas to a powerful energy resource.
The EPA has developed a federal outreach program (CMOP), working collaboratively with the industry to promote the profitable recovery, utilization, and mitigation of waste mine methane, and has recognized RMG as a clean-burning fuel. Because RMG is released through mining activities, the recovery and use of RMG is considered emissions avoidance. RMG projects—including natural gas pipeline sales—have been included in major international carbon trading programs for over 15 years, including the Kyoto Protocol’s Clean Development Mechanism and Verra’s Verified Carbon Standard.
RMG is a targeted, ultra-low carbon intensity energy recognized as credit generating resource under multiple state Renewable Portfolio Standards including Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Colorado, and Utah. Additionally, the Climate Action Reserve, California Air Resource Board (“CARB”), and American Carbon Registry each have project verification and credit generation protocols for RMG projects, which include peer-reviewed, rigorous monitoring, and quantification procedures that allow for a robust expression of the benefits of RMG’s methane avoidance.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National laboratory performed a detailed life cycle analysis on RMG. Argonne’s scientists included a Mine Methane/ Waste Methane Utilization within the published R&D GREET recognizing the methane emissions avoidance benefit of capturing and utilizing RMG.
The coal producing regions—where workers are challenged disproportionately by the energy transition—could lead our country in methane emissions reductions, while also driving economic value in their communities. Local governments will benefit from new tax revenue and income, thanks to the capital-intensive nature of the buildout of RMG capture and processing systems. Capturing all forecasted emissions from RMG would reduce emissions by a total of 236 million metric tonnes of CO2e over a 20-year timeframe and create over 500 jobs annually through 2041. 2
For more information visit www.wastegascapture.com
Every year CNX captures RMG CO2e emissions equivalent to:
-
 2.1m
2.1m
2.1 million gasoline powered vehicles 1.1m
1.1m
Over 1.1m homes’ energy use for 1 year 1.7m
1.7m
Over 1.7m homes’ electricity use for 1 year 21m
21m
21 million barrels of oil consumed
1. [Kholod et al.]—Kholod, N., Evans, M., Pilcher, R., et al. (February 2020). Global methane emissions from coal mining to continue growing even with declining coal production. Journal of Cleaner Production, 256.
2. West Virginia Development to Capture Mine Methane Emissions: IMPLAN, FTI Consulting; 2023